IDS Software Suite 4.96.1
Gigabit Ethernet was developed on the basis of the Fast Ethernet (100 Mbps) standard. In June 1999, the IEEE 802.3ab 1000 Mbps standard was defined by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). Using at least Cat 5e copper cables, transmission rates of 1 Gbps can be obtained. This makes Gigabit Ethernet 10 times faster than Fast Ethernet. The main advantages of Gigabit Ethernet include:
•Higher bandwidth, allowing for better network performance and the elimination of bottlenecks
•Full-duplex capability virtually doubles the effective bandwidth
•Low purchasing and operating costs through the use of common hardware
•Full compatibility with the large number of installed Ethernet and Fast Ethernet nodes
•Fast transfer of large amounts of data over the network

Fig. 76: Structure of a Cat 5e cable
For connecting Gigabit Ethernet cables, RJ45 connectors are used. The following illustrations show schematic views of an RJ45 socket (with cable configuration) and of an RJ45 plug.
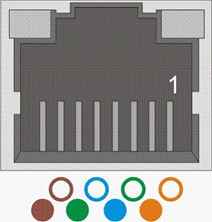
Fig. 77: RJ45 socket (EU type acc. to EIA/TIA-568B)
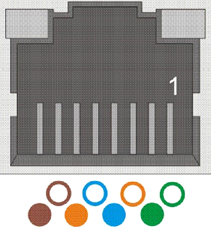
Fig. 78: RJ45 socket (US type acc. to EIA/TIA-568A)
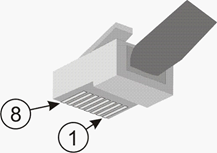
Fig. 79: RJ45 plug
|
The GigE uEye camera automatically recognizes whether an Ethernet cable with crossed wiring or straight wiring is connected. The camera adjusts accordingly. |
