Imaging outcomes depend crucially on contrast. It is only by making a feature “pop” relative to the larger image field in which the feature lies, that the feature can be optimally identified by machine vision software.
While sensor choice, lensing, and lighting are important aspects in building machine vision solutions with effective contrast creation, effective selection and application of filters can provide additional leverage for many applications. Often overlooked or misunderstood, here we provide a first-look at machine vision filter concepts and benefits.
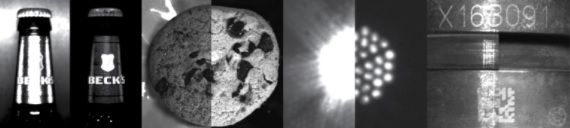
In the 4 image pairs above, each left-half image was generated with the same sensor, lighting, and exposure duration as the corresponding right-half images. But the right-half images have had filters applied to reduce glare or scratch-induced scatter, separate or block certain wavelengths, for example. If your brain finds the left-half images to be difficult to discern, image processing software wouldn’t be “happy” with the left-half either!
While there are also filtering benefits in color and SWIR imaging, it is worth noting that we started above with examples shown in monochrome. Surprising to many, it can often be both more effective and less expensive to create machine vision solutions in the monochrome space – often with filters – than in color. This may seem counter-intuitive, since most humans enjoy color vision, and use if effectively when driving, judging produce quality, choosing clothing that matches our skin tone, etc. But compared to using single-sensor color cameras, monochrome single sensor cameras paired with appropriate filters:
- can offer higher contrast and better resolution
- provide better signal-to-noise ratio
- can be narrowed to sensitivity in near-ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared spectrums
These features give monochrome cameras a significant advantage when it comes to optical character recognition and verification, barcode reading, scratch or crack detection, wavelength separation and more. Depending on your application, monochrome cameras can be three times more efficient than color cameras.
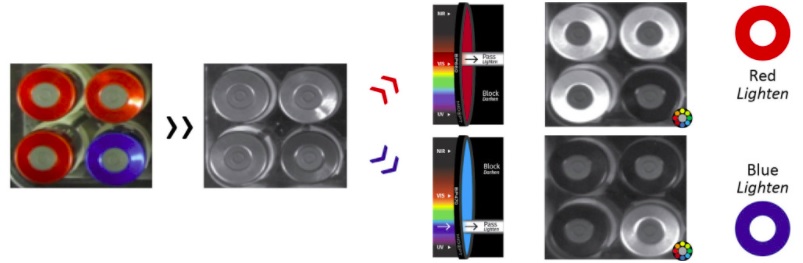
Color cameras may be the first thought when separating items by color, but it can be more efficient and effective to use a monochrome camera with a color bandpass filter. As shown above, to brighten or highlight an item that is predominantly red, using a red filter to transmit only the red portion of the spectrum can be used, blocking the rest of the transmitted light. The reverse can also work, using a blue filter to pass blue wavelengths while blocking red and other wavelengths.
Here we have touched on just a few examples, to whet the appetite. We anticipate developing a Tech Brief with a more in depth treatment of filters and their applications. We partner with Midwest Optical to offer you a wide range of filters for diverse application solutions.
1st Vision’s sales engineers have an average of 20 years experience to assist in your camera selection. Representing the largest portfolio of industry leading brands in imaging components, we can help you design the optimal vision solution for your application.
1st Vision is the most experienced distributor in the U.S. of machine vision cameras, lenses, frame grabbers, cables, lighting, and software in the industry.
