Who needs 360° optics? Granted, it’s specialized stuff. Innovative lenses in Opto Engineering’s series enable single-camera inspection of objects many users might not have thought possible! For example, a Bi-Telecentric system uses mirrors to image all 4 sides of an object at once, without moving the camera or the object. Or a boroscope gets the optics and a light inside a tight space, creating a panoramic view of the interior.
Even experienced machine vision professionals may never have seen or heard of some of these specialized optics. Unless one knows of such lens systems, one might try to design a multi-camera system for an application, when in fact a single camera could have been used!
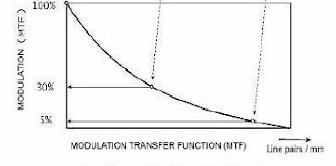
In the segments below, we highlight categories for which there are lens series available, together with representative images, diagrams, and texts. The goal here is not a master class in optics – just an overview to raise awareness.
Pericentric lenses
Opto Engineering provides pericentric lenses, allowing 360° by 180° FOV from a position above an object. That provides 360° top and lateral views with a single camera. The PC Series, with five choices, are designed to perform complete inspection of objects up to 60 mm in diameter. Typical applications include bottleneck thread inspection and data matrix reading – the code will always be properly imaged regardless of its position.
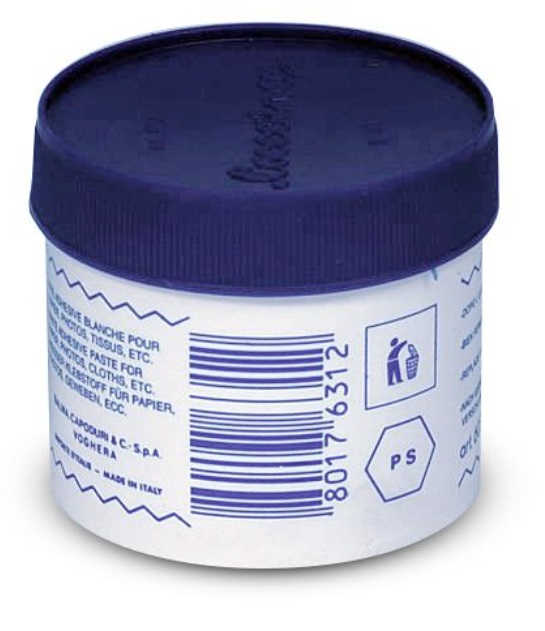

Suppose you produce and pack a product in a plastic container such as the one shown here. Quality control inspections may require verifying each container is labeled with print, graphical, and/or coded information. Image courtesy Opto Engineering.
Below we see the top and sides imaged in a single exposure, using a PC lens:
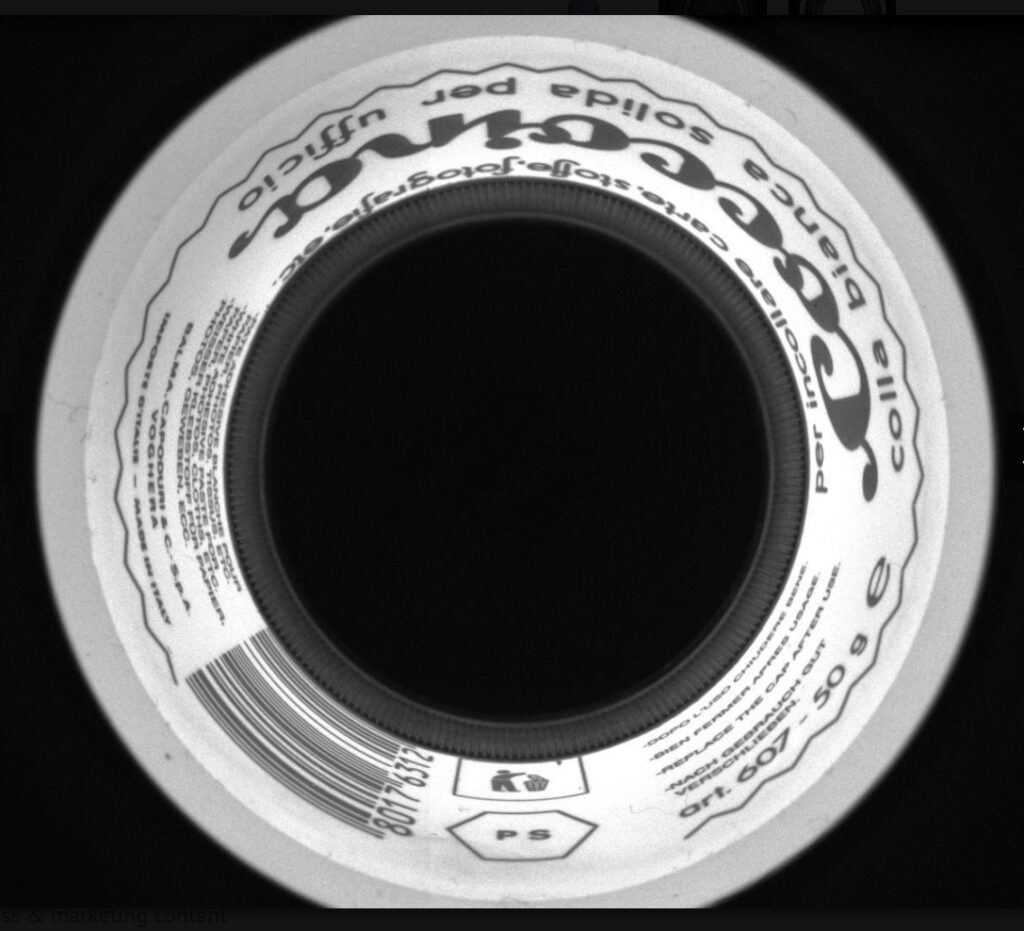

The PCCD Series, with four members, enables the 360° side view of small objects (sample diameter 7 – 35 mm). Perfect for bottle cap and can inspection.
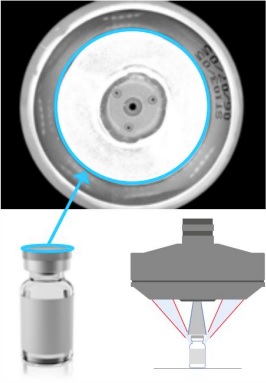
Above, the top image is generated from a lens that uses both reflection and refraction to image the vial’s interior as well as the exterior “shoulder”. The interior check is for any impurities before filling, and the exterior aspect is to obtain OCR characters or bar codes for tracking.
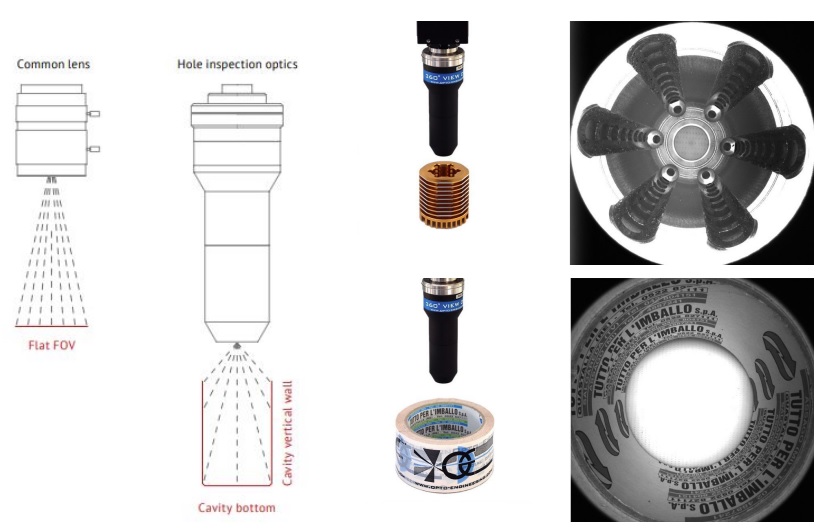
Hole inspection lenses
The PCHI Series includes 10 members, covering a range of sensor sizes, and includes a liquid lens option for adjustable focus control. Unlike a common lens with a flat field of view (FOV), these lenses provide a focused view of both the cavity bottom as well as the interior sidewalls! Perfect for thread inspection or cavity checks for contamination from above the cavity entrance.
Bi-Telecentric lens systems
Many are familiar with telecentric lenses, which hold magnification constant, regardless of an object’s distance or position in the field of view. Consider Opto Engineering’s Bi-Telecentric Series, TCCAGE. Using multiple mirrors, parts can be measured and inspected horizontally from each 90, with no rotation required. Two different illumination devices are built into the system to provide either backlight or direct part illumination. In the example to the right, syringes are inspected for length and angle from all 4 directions.
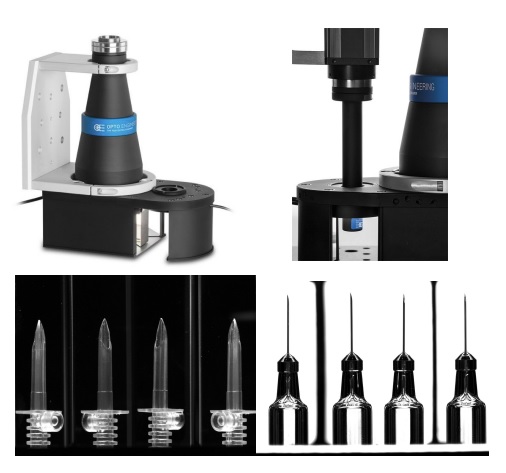

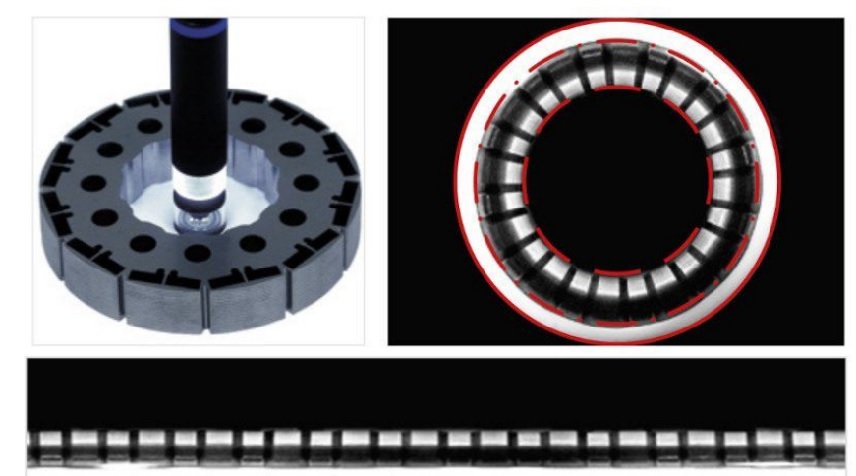
Boroscopic probes
A boroscope gets the optics into tight spaces, for panoramic cavity imaging from the inside. The PCBP series includes built-in compact illumination. It’s ideal for 360 degree inspection of interiors with static parts.
Focus controls
In addition to fixed focus and manual focus (with lockring) options, some lenses in the PCHI and PCBP Series include Adjustable Focus (AF) features. With liquid lens technology, using AF these lenses with varying product sizes and dimensions just got easier. With millisecond repositioning, it allows extremely fast changes to focus to allow you to dial in the exact position on multiple size products or sizes for inspection of an even wider range of SKU with a single system.
If your imaging application can be solved with more conventional lenses, lucky you. But if your requirements might otherwise be impossible to address, or seemingly need two or more separate cameras, or complex rotation controls and multiple exposures, call us at 978-474-0044. You might not have realized there are specialized optics designed precisely for your type of application!
1st Vision’s sales engineers have over 100 years of combined experience to assist in your camera and components selection. With a large portfolio of lenses, cables, NIC card and industrial computers, we can provide a full vision solution!