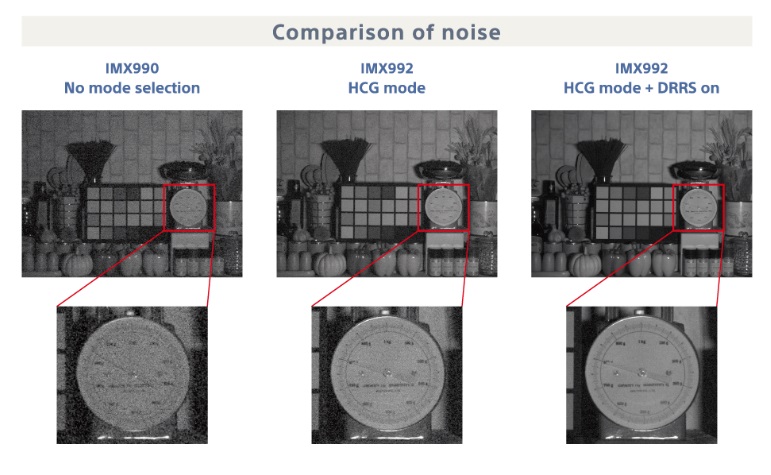
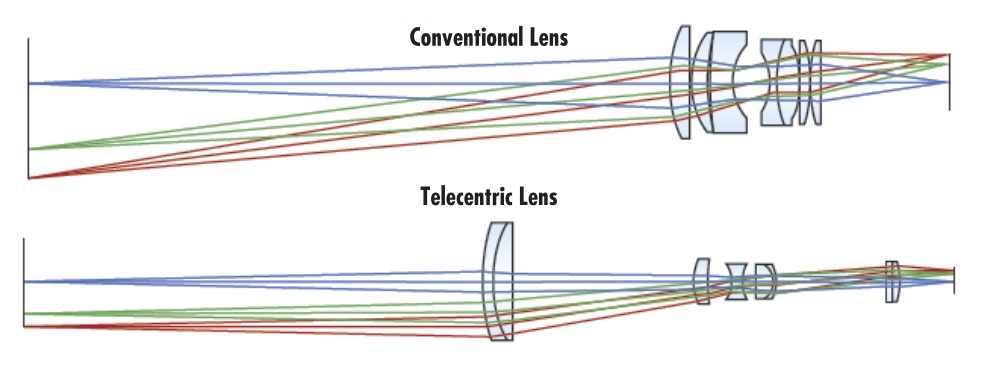
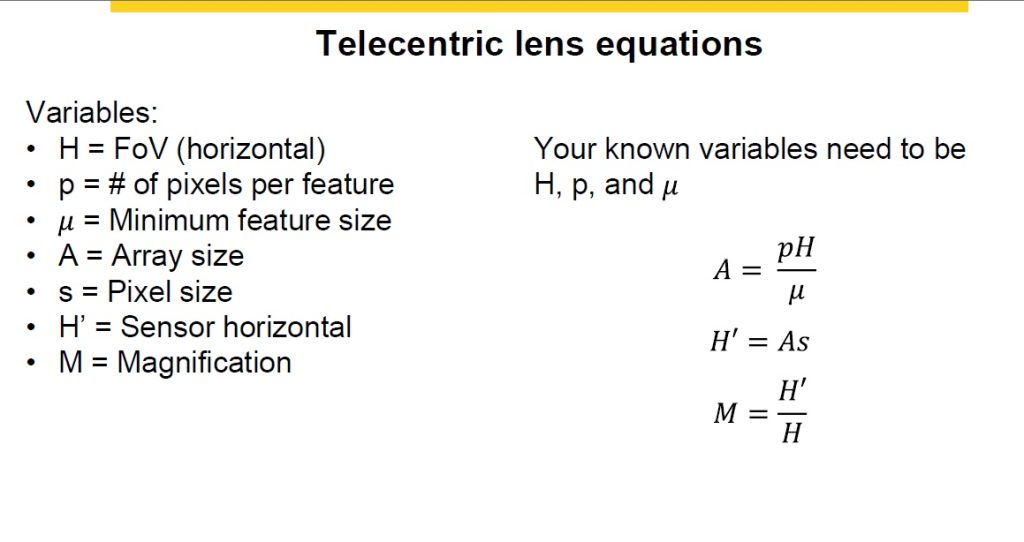
New interface options arrive so frequently that trying to keep up can feel like drinking water from a fire hose. While data transfer rates are often the first characteristic identified for each interface, it’s important to also note distance capabilities, power requirements, EMI reduction, and cost.
Which interfaces are we talking about here?
This piece is NOT about GigE Vision or Camera Link. Those are both great interfaces suitable for medium to long-haul distances, are well-understood in the industry, and don’t require any new explaining at this point.
We’re talking about embedded and short-haul interface considerations
Before we define and compare the interfaces, what’s the motivation? Declining component costs and rising performance are driving innovative vision applications such as driver assistance cameras and other embedded vision systems. There is “crossover” from formerly specialized technologies into machine vision, with new camera families and capabilities, and it’s worth understanding the options.

How shall we get a handle on all this?
Each interface has standards committees, manufacturers, volumes of documentation, conferences, and catalogs behind it. One could go deep on any of this. But this is meant to be an introduction and overview, so we take the following approach.
- Let’s identify each of the 4 interfaces by name, acronym, and a few characteristics
- While some of the links jump to a specific standard’s full evolution (e.g. FPD-Link including Gen 1, 2, and 3), per the blog header it’s the current standards as of Fall 2024 that are compelling for machine vision applications: CSI-2, GMSL2, and FPD-Link III, respectively
- Then we compare and contrast, with a focus on rules of thumb and practical guidance
If at any point you’ve had enough reading and prefer to just talk it through:
FPD-Link III – Flat Panel Display Link
A free and open standard, FPD-Link has classically been used to connect a graphics display unit (GPU) to a laptop screen, LCD TV, or similar display.
FPD-Link has subsequently become widely adopted in the automotive industry, for backup cameras, navigation systems, and driver-assistance systems. FPD-Link exceeds the automotive standards for temperature ranges and electrical transients, making it attractive for harsh environments. That’s why it’s interesting for embedded machine vision too.
GMSL2 – Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link

GMSL is widely used for video distribution in cars. It is an asymmetric full duplex technology. Asymmetric in that it’s designed to move larger volumes of data downstream, and smaller volumes upstream. Plus power and control data, bi-directionally. Cable length can be up to 15m.
CSI-2 – Camera Serial Interface (Gen. 2)

As the Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI) standard for communications between a camera and host processor, CSI-2 is the sweet spot for applications in the CSI standards. CSI-2 is attractive for low power requirements and low electromagnetic interference (EMI). Cable length is limited to about 0.5m between camera and processor.
USB – USB3 Vision

USB3 Vision is an imaging standard for industrial cameras, built on top of USB 3.0. USB3 Vision has the same plug-and-play characteristics of GigE Vision, including power over the cable, and GenICam compliance. Passive cable lengths are supported up to 5m (greater distances with active cables).
Compare and contrast
In the spirit of keeping this piece as a blog, in this compare-and-contrast segment we call out some highlights and rules-of-thumb. That, together with engaging us in dialogue, may well be enough guidance to help most users find the right interface for your application. Our business is based upon adding value through our deep knowledge of machine vision cameras, interfaces, software, cables, lighting, lensing, and applications.
CABLE LENGTHS COMPARED(*):
- CSI-2 is limited to 0.5m
- USB3 Vision passive cables to 5m
- FPD-Link distances may be up to 10m
- GMSL cables may be up to 15m
(*) The above guidance is rule-of-thumb. There can be variances between manufacturers, system setup, and intended use, so check with us for an overall design consultation. There is no cost to you – our sales engineers are engineers first and foremost.
BANDWIDTH COMPARED#:
- USB3 to 3.6 Gb/sec
- FPD-Link to 4.26 Gb/sec
- GMSL to 6 Gb/sec
- CSI-2 to 10 Gb/sec
(#) Bandwidth can also vary by manufacturer and configuration, especially for MIPI and SerDes [SerializerDeserializer], and per chipset choices. Check with us for details before finalizing your choices.
RULES OF THUMB:
- CSI-2 often ideal if you are building your own instrument(s) with short cable length
- USB3 is also good for building one’s own instruments when longer distances are needed
- FPD-Link has great EMI characteristics
- GMSL is also a good choice for EMI performance
- IF torn between FPD-Link vs. GMSL, note that there are more devices in the GMSL universe, so that might skew towards easier sourcing for other components
1st Vision’s sales engineers have over 100 years of combined experience to assist in your camera and components selection. With a large portfolio of cameras, lenses, cables, NIC cards and industrial computers, we can provide a full vision solution!
About you: We want to hear from you! We’ve built our brand on our know-how and like to educate the marketplace on imaging technology topics… What would you like to hear about?… Drop a line to info@1stvision.com with what topics you’d like to know more about.