IDS Software Suite 4.96.1
Binning is a function that averages or adds multiple sensor pixels to obtain a single value. This reduces the amount of data to be transferred and enables higher camera frame rates. The captured image has a lower resolution but still the same field of view compared to the full-resolution image. This mode can be used as a fast preview mode for high-resolution cameras. Depending on the binning method (adding or averaging), the image can change:
•If the pixel values are added, the image brightness increases.
•If the pixel values are averaged, the image noise is reduced.
In addition, it is distinguished if a sensor performs monochrome or color binning:
•Color binning, as performed by most color sensors, combines only pixels of the same color (see also the Color filter (Bayer filter) chapter). For some monochrome sensors, the camera also performs color binning, resulting in slight artifacts.
•Most monochrome sensors and some color sensors combine neighboring Bayer pattern pixels; in this case, the color information gets lost (mono binning).
Depending on the model, uEye cameras support different binning factors. Binning of horizontal and vertical pixels can be enabled independently.
The Camera and sensor data chapter lists the binning methods and factors the individual camera models support.
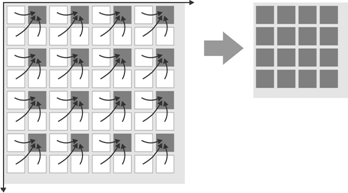
Fig. 36: Binning on monochrome sensors
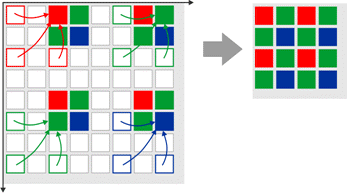
Fig. 37: Binning on color sensors